Table of Contents
What is Knee Arthritis?
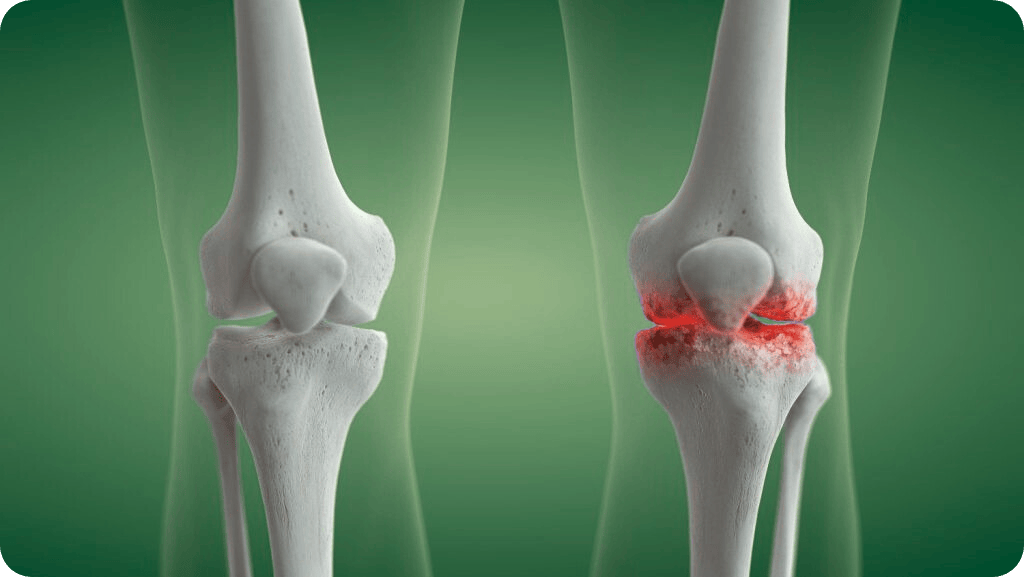
Knee arthritis is a leading cause of knee pain for adults over 40. The most common type, osteoarthritis, occurs when the smooth cartilage within the knee wears away and bones begin rubbing together causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. Other types include rheumatoid arthritis and post-injury arthritis, both of which may impact your knee health.
Types of Knee Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis (OA): The most common form, where protective cartilage gradually breaks down from wear and tear.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the joint lining, causing inflammation and damage.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Can develop months or years after injuries like fractures or ligament tears.
- Gout & Pseudogout: Less common types, resulting from crystal build-up in the joint; symptoms may include sudden pain and swelling.
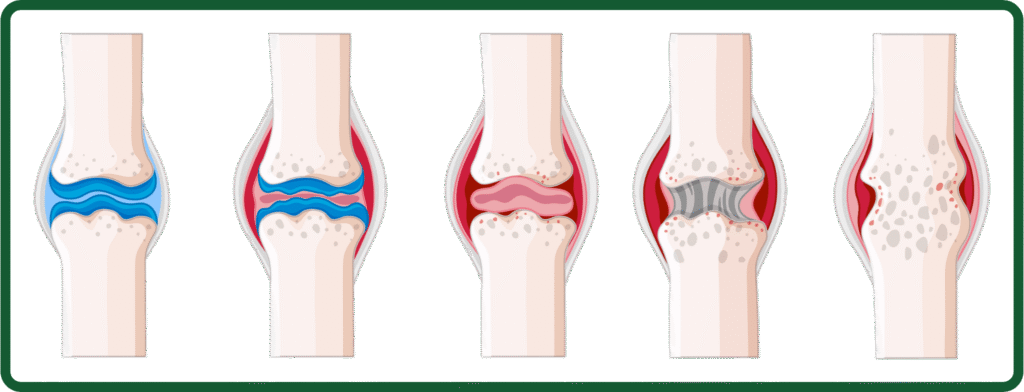
What Causes Knee Arthritis?
- Natural ageing and cartilage wear
- Family history of arthritis
- Previous injuries or fractures
- Carrying extra weight (adds stress to joints)
- Inflammatory conditions (such as rheumatoid arthritis)
- Repetitive movement or high-impact sports
Symptoms & Diagnosis
| Early Symptoms | Chronic Symptoms | Special Flare-Ups |
| Mild pain after walking or climbing stairs | Frequent pain, even at rest or during night | Sudden, severe pain and swelling (gout/pseudogout) |
| Morning or after-rest stiffness | Ongoing stiffness and movement difficulty | More warmth and redness (RA) |
| Occasional swelling | Regular swelling, instability (“giving way”) | Can follow injury or overuse |
| Grinding feel when moving |
DIAGNOSIS : Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination and history. Tests may include:
- X-rays: To assess cartilage and joint space.
- MRI scans: For detecting early arthritis or soft tissue injury.
- Blood tests: To rule out inflammatory causes like RA.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on arthritis type, severity, and your lifestyle.
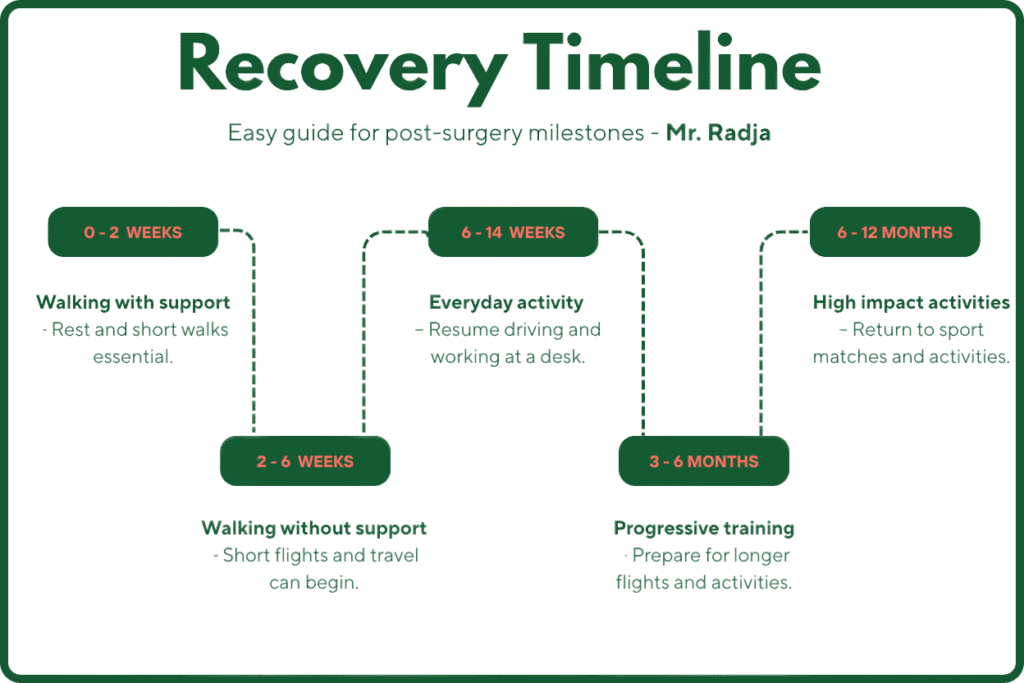
Recovery Timeline
Summary
Knee arthritis affects 1 in 5 adults over 45 in England (18.2%), but early diagnosis and treatment can make a real difference. Most people do well with lifestyle adjustments, exercise, and therapy whereas surgery is needed only for a minority.
If you’re in Manchester and suffering knee pain or stiffness, schedule a specialist assessment with Mr. Radja and take the first step toward lasting joint health.